Section 1 – Introduction: Wegovy in Obesity Management
Obesity is a chronic, relapsing disease affecting over 650 million adults globally, with strong associations to cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, cancer, and reduced quality of life.
Previous pharmacological interventions for obesity often achieved <10% weight loss—modest compared to bariatric surgery. Wegovy represents a paradigm shift, offering average weight loss of 15–17% in non-diabetic adults in pivotal trials, approaching surgical efficacy but with the convenience of weekly self-injection.
Wegovy is 1 of 3 weight-loss injections, the others being Saxenda (liraglutide) and Mounjaro (tirzepatide).
What is Wegovy?
Wegovy® is the brand name for semaglutide 2.4 mg, a once-weekly injectable medication developed by Novo Nordisk for chronic weight management.
It gained U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for chronic weight management in June 2021, making it the first new anti-obesity medication to receive FDA clearance in nearly a decade with demonstrated double-digit weight loss in phase 3 trials.
While originally developed as an antidiabetic drug under the brand Ozempic® (semaglutide 0.5–1 mg), the higher-dose 2.4 mg formulation was optimized and clinically evaluated specifically for obesity treatment.
FDA and Global Approvals
| Regulatory Body | Indication Approved | Date of Approval |
|---|---|---|
| FDA (USA) | Chronic weight management in adults with BMI ≥30 kg/m², or BMI ≥27 kg/m² with ≥1 weight-related comorbidity | June, 2021 |
| FDA (USA) | For adolescents (≥12 years) | December 2022 |
| EMA (Europe) | Chronic weight management in adults meeting similar BMI/comorbidity criteria | January 2022 |
| TGA (Australia) | Chronic weight management | September 2022 |
| Health Canada | Chronic weight management | November 2022 |
| NICE (UK) | Recommendation with restricted NHS availability through specialist weight management services | March 2023 |
| Japan PMDA | Not yet approved for obesity (as of 2025), semaglutide available for T2DM only | — |
| India CDSCO | Not approved for obesity; approved for T2DM as Ozempic (1 mg). Off-label use possible under medical supervision | — |
How does Wegovy work?
Wegovy (semaglutide) is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, structurally similar to the naturally occurring incretin hormone GLP-1, that helps regulate appetite and food intake.
When Wegovy activates the GLP-1 receptors in the brain, it:
- Reduces appetite by signaling satiety centers in the brain.
- Slows gastric emptying, so food stays in the stomach longer, helping you feel fuller.
- Decreases energy intake, leading to reduced calorie consumption.
Together, these effects promote effective weight loss. Unlike the short-acting natural GLP-1 hormone, Wegovy is engineered to last longer in the body, allowing for once-weekly dosing with sustained appetite regulation.
Wegovy is a prescription medicine and should be used together with a decreased-calorie meal plan and increased physical activity to help with weight management.
Section 2 – Semaglutide: A GLP-1 Receptor Agonist
Semaglutide and the Incretin Pathway
Semaglutide is a long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist (RA). GLP-1 is an incretin hormone secreted by intestinal L-cells in response to nutrient ingestion. It plays a key role in:
- Enhancing glucose-dependent insulin secretion
- Suppressing glucagon release
- Delaying gastric emptying
- Reducing appetite through central nervous system signaling
In people with obesity or type 2 diabetes, endogenous GLP-1 secretion and receptor responsiveness may be reduced. Semaglutide compensates by activating GLP-1 receptors at pharmacological levels, amplifying satiety signals and improving postprandial glucose handling.
Structural Modifications for Long-Acting Action
Natural GLP-1 has a very short half-life of about 2 minutes, as it is rapidly broken down by the body's enzymes and cleared by the kidneys. Semaglutide has been structurally modified to overcome this limitation, which protects it from being broken down too quickly and helps it stay in the bloodstream for several days. These modifications significantly extend the half-life of semaglutide to around 165 hours, making once-weekly dosing possible.
Pharmacokinetic Summary Table
| Parameter | Semaglutide 2.4 mg (Wegovy) |
|---|---|
| Mechanism | GLP-1 receptor agonist |
| Half-life | ~165 hours (~7 days) |
| Peak plasma concentration | 1–3 days post-injection |
| Bioavailability | ~89% (subcutaneous) |
| Metabolism | Proteolytic cleavage, β-oxidation of fatty acid side chain |
| Elimination | Primarily via urine and feces as small peptides and amino acids |
| Dosing frequency | Once weekly |
Section 3 – The Clinical Foundation of Wegovy
The efficacy and safety of semaglutide 2.4 mg for chronic weight management have been extensively evaluated in the Semaglutide Treatment Effect in People with obesity (STEP) clinical trial program. These large, multicenter, randomized controlled trials (RCTs) form the cornerstone of Wegovy’s evidence base.
STEP 1 Trial – Landmark Weight Loss in Adults without Diabetes
- Design: Double-blind, placebo-controlled, 68-week trial
- Population: 1,961 adults with obesity (BMI ≥30) or overweight (BMI ≥27 with ≥1 weight-related comorbidity), without type 2 diabetes
- Intervention: Semaglutide 2.4 mg once weekly + lifestyle intervention vs placebo + lifestyle intervention
- Results:
- Mean weight loss: 14.9% with semaglutide vs 2.4% with placebo
- ≥5% weight loss: 86% of semaglutide group vs 31% placebo
- Significant improvements in waist circumference, blood pressure, and CRP
STEP 2 Trial – Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
- Population: 1,210 adults with obesity/overweight and type 2 diabetes
- Results:
- Mean weight loss: 9.6% with semaglutide 2.4 mg vs 3.4% with placebo
- HbA1c reduction: −1.6 percentage points (semaglutide) vs −0.4 (placebo)
- Interpretation: Weight loss was less than in STEP 1, consistent with T2DM populations, but still clinically significant.
STEP 3 Trial – Intensive Behavioral Therapy (IBT)
- Population: 611 adults with obesity/overweight
- Intervention: Semaglutide 2.4 mg + IBT vs placebo + IBT
- Results:
- Mean weight loss: 16.0% vs 5.7% placebo
- 86.6% achieved ≥5% weight loss
- Implication: Adding semaglutide to structured behavioral programs yields synergistic benefits.
STEP 4 Trial – Maintenance of Weight Loss
- Design: Run-in phase where all participants received semaglutide 2.4 mg for 20 weeks, then randomized to continue drug or switch to placebo for 48 weeks.
- Results:
- Continued therapy: −7.9% additional weight loss
- Placebo switch: +6.9% weight regain
- Conclusion: Ongoing therapy is critical for maintaining weight loss.
STEP 5 Trial – Two-Year Data
- Population: 304 adults with obesity/overweight without T2DM
- Duration: 104 weeks
- Results:
- Mean weight loss: −15.2% at week 104 vs −2.6% placebo
- Sustained improvements in cardiometabolic markers
STEP TEENS Trial – Adolescent Obesity
- Population: 201 adolescents aged 12–17 years with obesity
- Results:
- BMI reduction: −16.1% with semaglutide vs +0.6% placebo at 68 weeks
- 77% achieved ≥5% BMI reduction
- Significance: Semaglutide is now FDA-approved for adolescents ≥12 years with obesity.
Meta-Analysis & Real-World Data
- Pooled STEP trial analysis shows mean weight loss of 12–15% in adults without T2DM and 6–9% in those with T2DM.
- Observational studies report similar results in clinical practice, confirming trial reproducibility.
Section 4 – Benefits of Using Wegovy (Semaglutide 2.4 mg)
Wegovy’s benefits extend beyond significant weight reduction. Clinical and real-world evidence indicate that its effects span metabolic health, cardiovascular risk reduction, quality-of-life improvement, and potential organ protection.
1. Significant and Sustained Weight Loss
- Magnitude: In the STEP trials, Wegovy achieved 14.9–17.4% mean weight loss in adults without T2DM over 68 weeks — the highest among GLP-1–only therapies.
- Durability: STEP 5 showed sustained ~15% loss over 104 weeks when treatment continued.
- Responder rate: 86–91% achieved ≥5% weight loss — a clinically meaningful benchmark for improved metabolic outcomes.
2. Obesity-Related Cardiometabolic Risk Reduction
- Blood pressure: Average reductions of ~6 mmHg systolic and ~3 mmHg diastolic in STEP 1.
- Lipid profile: Decreases in triglycerides (~20%), LDL cholesterol (~5–7%), and increases in HDL cholesterol (~5%).
- Inflammation: Lower high-sensitivity CRP (−40% from baseline in STEP 1), indicating systemic anti-inflammatory effect.
- Glycemic control: Modest HbA1c improvement (−0.5% in non-diabetic populations) and greater impact in T2DM patients (−1.6%).
3. Appetite Regulation and Eating Behavior
- Acts centrally on the hypothalamus to enhance satiety and reduce cravings.
- Clinical participants reported decreased frequency of snacking, reduced preference for high-fat/high-sugar foods, and smaller portion sizes.
- This behavioral shift is critical for maintaining long-term weight loss.
4. Non-Scale Benefits
- Improved mobility: Greater ease in daily physical activities.
- Better sleep: Reductions in obstructive sleep apnea severity scores in early studies.
- Joint relief: Weight reduction alleviates osteoarthritis symptoms.
- Fertility and reproductive health: Emerging evidence suggests improvement in menstrual regularity in women with obesity-related anovulation.
- Improved Mental Health: Decreased incidence of obesity-related depression symptoms in some patients, likely linked to improved self-image and mobility.
5. Public Health Impact
- Wide use of Wegovy could reduce obesity-related morbidity at a population level, lowering long-term healthcare costs related to T2DM, cardiovascular disease, and certain cancers.
- In high-risk populations, it may serve as both treatment and prevention for metabolic syndrome progression.
- Wegovy works by controlling metabolism and reducing appetite, leading to an average additional weight loss of about 12–15% over 68 weeks in adults without diabetes. This level of weight reduction is close to what is seen with bariatric surgery in people with moderate obesity and is greater than the effect of older weight-loss medicines.
Section 5 – Who Can Use Wegovy?
Wegovy (semaglutide 2.4 mg) is not for everyone — it is intended for patients meeting specific BMI and health criteria, as obesity pharmacotherapy is part of a chronic disease management approach rather than cosmetic weight loss.
Clinical Use and Dosage Recommendations
Wegovy is indicated as an adjunct to a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity for chronic weight management in:
- Adults with BMI ≥30 kg/m² (obesity)
- Adults with BMI ≥27 kg/m² (overweight) plus at least one weight-related comorbidity such as:
- Hypertension
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM)
- Dyslipidemia
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Cardiovascular disease
- Adolescents (≥12 years) with BMI at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex (based on CDC growth charts)
Approved Dosages
- 0.25 mg / 0.5 mL (initiation dose)
- 0.5 mg / 0.5 mL
- 1.0 mg / 0.5 mL
- 1.7 mg / 0.75 mL
- 2.4 mg / 0.75 mL (maintenance dose)
The 2.4 mg weekly dose is the FDA- and EMA-approved maintenance dose for weight management, following a stepwise dose escalation to minimize gastrointestinal side effects.
Eligibility Criteria – Practical Clinical Use
Ideal candidates for Wegovy are:
- Patients with significant obesity-related health risks who have not achieved adequate weight loss through lifestyle intervention alone
- Adults and adolescents motivated to engage in sustained dietary and activity modifications alongside medication use
- Patients without contraindications and who are capable of self-injection or have support for administration
Note: Wegovy is not indicated for treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and has not been studied in patients with a history of pancreatitis.
Section 6 – Guidelines for Safe Use of Wegovy (Semaglutide 2.4 mg)
Correct administration and adherence to dosing protocols are critical for maximizing Wegovy’s benefits while minimizing side effects. The following guidelines align with the FDA-approved prescribing information and best clinical practices.
Route of Administration
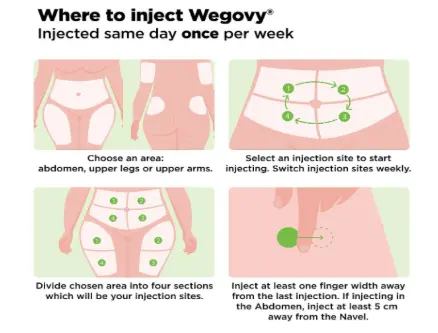
- Subcutaneous injection only
- Common sites: abdomen, front of the thigh, upper arm
- Rotate injection sites weekly to reduce risk of local reactions
- Avoid injecting into areas with bruises, scars, or hardened skin
Self-Administration Technique
Most patients can self-inject using the single-use prefilled Wegovy pen after proper training by a healthcare provider.
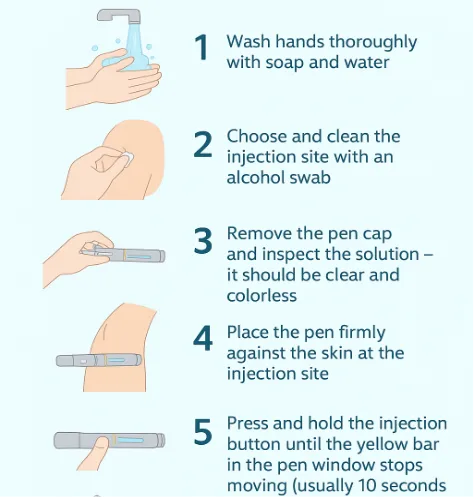
- Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water.
- Choose and clean the injection site with an alcohol swab.
- Remove the pen cap and inspect the solution — it should be clear and colorless.
- Place the pen firmly against the skin at the injection site.
- Press and hold the injection button until the yellow bar in the pen window stops moving (usually 10 seconds).
- Remove the pen and dispose of it in a sharps container.
- Do not reuse pens — each is single-use only.
Dosing and Titration Schedule
To reduce gastrointestinal side effects, Wegovy dosing is escalated gradually:
| Weeks | Weekly Dose |
|---|---|
| 1–4 | 0.25 mg |
| 5–8 | 0.5 mg |
| 9–12 | 1.0 mg |
| 13–16 | 1.7 mg |
| Week 17+ | 2.4 mg (maintenance dose) |
Note: If patients cannot tolerate a dose during escalation, consider delaying progression for an additional 4 weeks. Do not increase the dose more rapidly than recommended.
When to Inject
- Once a week, on the same day each week
- Can be taken at any time of day, with or without meals
-
If a dose is missed:
- Administer within 5 days (120 hours) of the scheduled time
- If more than 5 days have passed, skip the missed dose and resume the regular schedule
Storage Instructions
- Store unused pens in a refrigerator (2°C–8°C)
- Do not freeze — discard if frozen
- After first use, pens may be stored at room temperature (up to 30°C) for 28 days
- Protect from light; keep cap on until ready to inject
Special Populations
- Pediatrics: Approved for adolescents ≥12 years with obesity; same titration schedule as adults
- Older adults (>65 years): No dose adjustment required; monitor for heightened GI sensitivity
- Renal impairment: No dose adjustment, but monitor closely in severe cases due to dehydration risk from GI side effects.
- Hepatic impairment: Use with caution; pharmacokinetics not significantly altered.
- Pregnancy/Lactation: Contraindicated — discontinue at least 2 months before planned conception due to long washout period
Key Administration Safety Tips
- Never share pens between patients — risk of transmission of infections
- Do not mix Wegovy with other injectables in the same syringe or injection site
- Educate patients to recognize signs of allergic reaction (e.g., rash, swelling, difficulty breathing)
Section 7 – Side Effects and Contraindications
While Wegovy (semaglutide 2.4 mg) is generally well tolerated, it is associated with predictable side effects — mostly gastrointestinal — that are dose-dependent and typically occur during the titration phase.
1. Common Side Effects (≥5% in trials)
| Adverse Event | Incidence (%) in STEP 1 | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Nausea | 44% | Most frequent; usually transient |
| Diarrhea | 30% | Improves with continued use |
| Vomiting | 24% | Dose-related |
| Constipation | 24% | May require dietary fiber or stool softeners |
| Abdominal pain | 20% | Typically mild |
| Dyspepsia | 9% | Managed with antacids if needed |
| Fatigue | 6% | Often during initial weeks |
| Headache | 6% | Self-limiting |
Clinical note: GI symptoms usually peak in the early dose escalation phase and resolve over time. Gradual titration and dietary adjustments (smaller meals, avoiding high-fat foods) can help.
2. Serious Adverse Effects
| Adverse Effect | Incidence | Clinical Guidance |
|---|---|---|
| Pancreatitis | Rare (<0.3%) | Discontinue if severe abdominal pain radiating to the back occurs |
| Gallbladder disease (cholelithiasis, cholecystitis) | 1.6% vs 0.7% placebo | Linked to rapid weight loss; monitor for biliary symptoms |
| Acute kidney injury | Rare | Often secondary to dehydration from GI events |
| Hypoglycemia | Uncommon unless combined with insulin or sulfonylureas | Monitor glucose in patients with T2DM |
| Hypersensitivity reactions | Rare | Includes anaphylaxis and angioedema |
3. Contraindications
Wegovy should not be used in:
- Patients with personal/family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC) or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN2)
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women
- Patients with known hypersensitivity to semaglutide or any excipients
- Patients with a history of serious hypersensitivity reactions to other GLP-1 RAs
4. Warnings & Precautions
- GI disease: Avoid in patients with severe gastroparesis
- Pancreatitis: Use caution in patients with a history of pancreatitis
- Gallbladder disease: Rapid weight loss may increase risk — monitor symptoms
- Diabetic retinopathy: May worsen in T2DM patients with pre-existing condition; gradual glucose improvement recommended
- Suicidal ideation: Rare reports in weight management trials — monitor mood and behaviour
Observed in rodent studies; relevance to humans is unknown, but precaution is warranted.
5. Risk Mitigation Strategies for HCPs
- Educate patients about expected GI side effects and gradual titration
- Encourage hydration to prevent dehydration-related complications
- Review warning signs for pancreatitis, gallbladder issues, and allergic reactions
- Schedule follow-up visits during titration to assess tolerance and adjust therapy as needed
Section 8 – How Wegovy Differs from Zepbound
While both Wegovy (semaglutide 2.4 mg) and Zepbound (tirzepatide up to 15 mg) are once-weekly injectable drugs approved for chronic weight management, they differ in their mechanism of action, clinical efficacy, and patient considerations.
Mechanism of Action
- Wegovy: GLP-1 receptor agonist only → mimics natural GLP-1 to suppress appetite, delay gastric emptying, and improve glucose control.
- Zepbound: Dual GLP-1 + GIP receptor agonist → combines GLP-1 effects with GIP-mediated insulin sensitization and enhanced fat metabolism.
Comparative Data
| Feature / Outcome | Wegovy (Semaglutide 2.4 mg) | Zepbound (Tirzepatide 15 mg) |
|---|---|---|
| Mean weight loss – non-diabetic adults | 14.9–17.4% (STEP 1–3) | 20.9–22.5% (SURMOUNT-1) |
| Mean weight loss – adults with T2DM | 9.6% (STEP 2) | 12.8–14.7% (SURMOUNT-2) |
| ≥5% weight loss rate | 86–91% | 85–91% |
| Trial duration | 68–104 weeks | 72 weeks |
| Average HbA1c reduction (T2DM) | −1.6% | −2.3% |
| Cardiometabolic effects | ↓ BP, ↓ CRP, improved lipids | Similar, possibly greater triglyceride reduction |
| FDA obesity approval date | June 2021 | November 2023 |
| Available doses | 0.25–2.4 mg weekly | 2.5–15 mg weekly |
Clinical Selection Considerations
Wegovy may be preferred if:
- Patient requires a drug with the longest post-marketing safety record among anti-obesity injectables.
- Cardiovascular risk reduction data is a priority.
- Gradual, well-documented weight loss is clinically acceptable.
Zepbound may be preferred if:
- The patient’s primary goal is maximum weight reduction in the shortest time frame and in patients without contraindications.
- They also require potent glucose lowering beyond GLP-1 effects.
- They have tolerated GLP-1 agents well but need additional efficacy.
Interpretation: Though Tirzepatide produces greater average weight loss than semaglutide in trials, both agents show high response rates and significant health benefits.
Section 9 – Access and Availability of Wegovy
Wegovy’s rollout has been influenced by global demand, manufacturing capacity, regulatory approvals, and pricing considerations. Its availability varies significantly between countries, and affordability remains a barrier in many markets.
- High global demand: The success of STEP trials has fueled demand, leading to widespread shortages.
- Market prioritization: Novo Nordisk has focused initial supplies on the US and select European countries.
- Scaling production: New facilities are being added, with supply expected to improve by late 2025.
India – Current Status
- As of mid-2025, Wegovy is not commercially marketed in India.
- Semaglutide (Ozempic) for T2DM is available in lower doses (0.25–1.0 mg) but off-label prescribing for obesity is uncommon and subject to clinical discretion.
- Indian regulatory approval for obesity indication is pending; anticipated in the coming years as global supply improves.
Key Barriers to Access
- High cost: Out-of-pocket expenses make access difficult for uninsured patients.
- Global supply imbalance: Preference for high-income markets delays rollout in low- and middle-income countries.
- Regulatory lag: Approval timelines remain slower in countries like India, South Africa, and parts of Southeast Asia.
Section 10 – Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on Wegovy
| Drug | Brand | Weight-loss Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Tirzepatide | Zepbound, Mounjaro | Up to 22.5% average weight loss |
| Semaglutide | Wegovy | Up to 14.9% average weight loss |
| Liraglutide | Saxenda | ~8% average weight loss |
| Phentermine-topiramate | Qsymia | 7–11% depending on dose |
| Naltrexone-bupropion | Contrave | ~5–9% average weight loss |
Conclusion
The introduction of Wegovy (semaglutide 2.4 mg) represents a transformative milestone in the pharmacological management of obesity — a condition now recognized as a chronic, relapsing disease that demands sustained intervention. By harnessing the incretin pathway through selective GLP-1 receptor activation, Wegovy has demonstrated sustained weight loss, coupled with improvements in blood pressure, lipid profile, glycemic control, and overall quality of life.
In the context of newer anti-obesity medications, particularly Zepbound (tirzepatide), Wegovy maintains a strong position. While Zepbound may offer greater mean weight loss in trial settings, Wegovy benefits from longer-term cardiovascular outcomes data and broader familiarity among healthcare providers. This positions it as a trusted first-line pharmacological option in specialist weight management protocols, especially for patients with cardiovascular risk factors or those requiring a well-characterized safety history.
However, access remains a key challenge. Strategic expansion of production facilities and progressive regulatory approvals will be pivotal in bridging these gaps and ensuring wider accessibility.
Wegovy is not a quick fix, but for the right patient, it can be a long-term partner in weight management and a vital tool in reducing the burden of obesity-related diseases worldwide.
References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. FDA approves new drug treatment for chronic weight management [Internet]. Silver Spring (MD): FDA; 2021.Available from: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-new-drug-treatment-chronic-weight-management
- Wilding JPH, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(11):989-1002.
- World Health Organization. Obesity and overweight fact sheet [Internet]. Geneva: WHO; 2023.Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight
- British Heart Foundation. Wegovy: your questions answered [Internet]. London: BHF; 2023.Available from: https://www.bhf.org.uk/informationsupport/heart-matters-magazine/medical/ask-the-experts/wegovy
- Nauck MA, Meier JJ. Incretin hormones: their role in health and disease. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2018;20(Suppl 1):5-21.
- Lau J, et al. Discovery of the once-weekly GLP-1 analogue semaglutide. J Med Chem. 2015;58(18):7370-7380.
- Knudsen LB, Lau J. The discovery and development of liraglutide and semaglutide. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2019;10:155.
- Jastreboff AM, et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:205-216.
- Davies M, et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2). Lancet. 2021;397(10278):971-984.
- Wadden TA, et al. Effect of subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo as an adjunct to intensive behavioral therapy on body weight. JAMA. 2021;325(14):1403-1413.
- Rubino D, et al. Effect of continued weekly subcutaneous semaglutide vs placebo on weight loss maintenance. JAMA. 2021;325(14):1414-1425.
- Garvey WT, et al. Two-year effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: the STEP 5 trial. Nat Med. 2022;28(10):2073-2081.
- Weghuber D, et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adolescents with obesity. N Engl J Med. 2022;387:2245-2257.
- Kushner RF, et al. Semaglutide 2.4 mg for the treatment of obesity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Obesity. 2022;30(1):40-50.
- Frías JP, et al. Tirzepatide versus semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2023;388:1839-1852.
- Novo Nordisk A/S. Wegovy® (semaglutide) prescribing information. Bagsværd (Denmark): Novo Nordisk; 2024.
- NICE. Semaglutide for managing overweight and obesity. TA875. London: NICE; 2023.
- European Medicines Agency. Wegovy – summary of product characteristics. Amsterdam: EMA; 2024.
- Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO). Indian drug regulatory updates. New Delhi: CDSCO; 2024.
- European Medicines Agency. Public assessment report – Wegovy. Amsterdam: EMA; 2024.
- GlobalData Pharma Intelligence. GLP-1 market outlook. London: GlobalData; 2025.
- Obesity Medicine Association. Top weight loss medications. Obesity Medicine Association; 2025 Jul 29. Available from: https://obesitymedicine.org/blog/weight-loss-medications


