Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes are the foundation of obesity treatment, focusing on long-term alterations in diet, physical activity, and behavior.
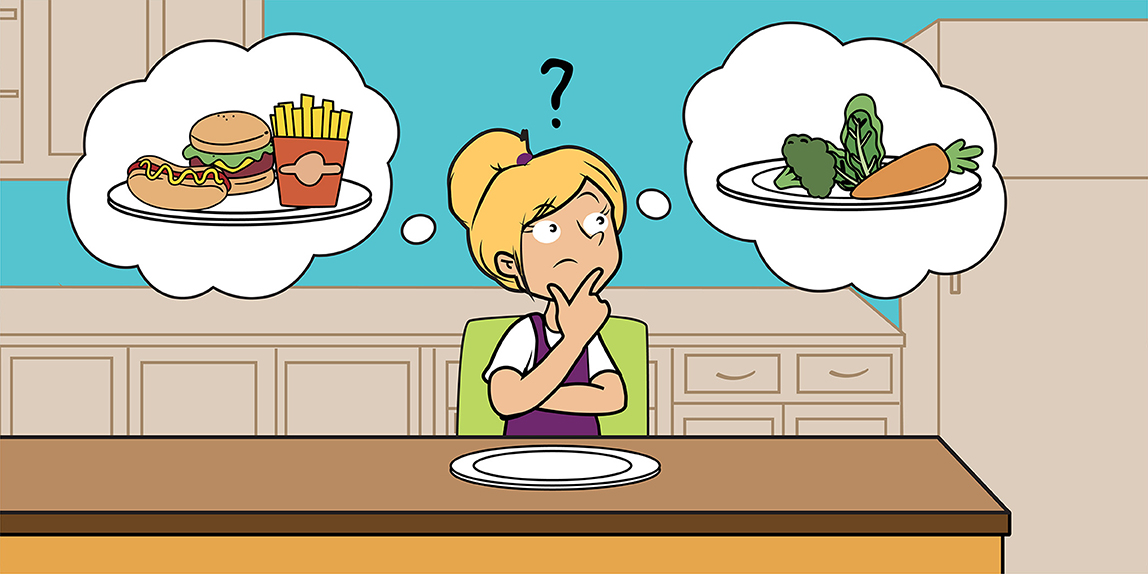
Dietary Changes:
- Caloric Reduction: Create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than expended.
- Healthy Eating Patterns: Adopt diets rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while minimizing processed foods and added sugars.
- Structured Meal Plans: Regular meal schedules help prevent overeating and promote metabolism.
Physical Activity:
- Aerobic Exercise: Engage in at least 150–300 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
- Strength Training: Incorporate resistance exercises to preserve muscle mass and boost metabolism.
- Daily Movement: Activities like walking, gardening, or climbing stairs enhance overall calorie expenditure.
Behavioral Therapy:
- Self-Monitoring: Track food intake, physical activity, and weight regularly.
- Goal Setting: Establish realistic and incremental goals for weight loss.
- Stress Management: Learn strategies to address emotional triggers for overeating.
Your body doesn't count the steps you take for a paycheck, but it treasures every move you make for joy and health.
Pharmacological Treatments
Medications can be an effective adjunct to lifestyle modifications, especially for individuals unable to achieve significant weight loss through diet and exercise alone. These are typically prescribed for individuals with a BMI ≥30 or ≥27 with obesity-related health conditions. Common medications include:
- Orlistat: Reduces fat absorption in the intestines.
- Liraglutide and Semaglutide: GLP-1 receptor agonists that suppress appetite and promote satiety.
- Naltrexone-Bupropion: Modulates brain pathways involved in hunger and cravings.
- Phentermine-Topiramate: Combines appetite suppression with enhanced calorie burning.
It is important to note that medications should be used under medical supervision. Regular follow-up is essential to monitor effectiveness and side effects.
Bariatric Surgery
Bariatric surgery is a highly effective option for individuals with severe obesity (BMI ≥40 or ≥35 with comorbidities) who have not achieved success with other treatments. These may include:
- Gastric Bypass: Reduces stomach size and alters digestion to limit calorie absorption.
- Sleeve Gastrectomy: Removes a portion of the stomach, reducing capacity and hunger hormone production.
- Adjustable Gastric Banding: Uses a band to restrict the stomach's size.
- Biliopancreatic Diversion with Duodenal Switch: Combines stomach reduction with significant intestinal bypass.
The benefits of weight loss interventions include significant and sustained weight reduction, which can lead to improvements in obesity-related health conditions such as diabetes and hypertension. However, these benefits come with the need for lifelong dietary changes and ongoing medical monitoring to ensure continued success and manage any potential health issues. While the long-term advantages are substantial, maintaining a healthy weight requires consistent effort and supervision.
Psychological and Emotional Support
Addressing psychological factors is crucial for the success of obesity treatment. This includes:
- Counseling: Individual or group therapy to manage emotional eating and body image issues.
- Support Groups: Provide motivation, accountability, and shared experiences.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps identify and modify unhealthy thought patterns and behaviors.
Endoscopic Procedures
Minimally invasive endoscopic techniques are emerging as alternatives to surgery for moderate to severe obesity. These may include:
- Intragastric Balloons: Temporarily placed in the stomach to reduce hunger.
- Endoscopic Sleeve Gastroplasty: Reduces stomach size using sutures.
These procedures are reversible but require adherence to lifestyle changes for long-term success.
Emerging Therapies
Advancements in medical research are continually expanding treatment options for obesity, such as:
- Anti-Obesity Vaccines: Targeting hormones involved in appetite regulation.
- Gene Therapy: Exploring genetic modifications to address obesity predisposition.
- Wearable Technology: Devices that monitor physical activity and provide real-time feedback.
Integrative and Complementary Approaches
Holistic approaches, when combined with conventional treatments, can enhance outcomes. These include:
- Mindfulness Practices: Yoga and meditation reduce stress and improve eating behaviors.
- Alternative Therapies: Acupuncture and biofeedback may complement weight loss efforts.
Dr. Shreya Sharma
Endocrinologist
"Langhanam param aushadham" is an ancient Sanskrit quote that means "Fasting is the best medicine". We can incorporate fasting in our daily lives by following "Time Restricted Eating" and aligning our Circadian rhythm with the Sun's energy!







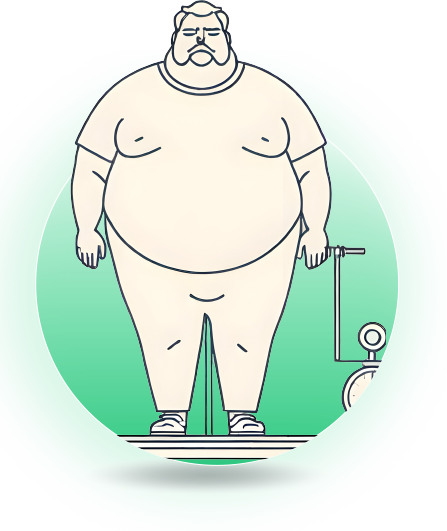
 Excess Body Fat: Visible accumulation, especially around the abdomen (central obesity).
Excess Body Fat: Visible accumulation, especially around the abdomen (central obesity).
 Reduced Mobility: Difficulty performing physical activities due to excess weight.
Reduced Mobility: Difficulty performing physical activities due to excess weight.
 Breathlessness: Even minimal exertion can result in shortness of breath.
Breathlessness: Even minimal exertion can result in shortness of breath.
 Chronic Fatigue: Persistent tiredness due to the physical strain on the body.
Chronic Fatigue: Persistent tiredness due to the physical strain on the body.
 Joint Pain: Excess weight places additional stress on joints, causing discomfort or conditions like osteoarthritis.
Joint Pain: Excess weight places additional stress on joints, causing discomfort or conditions like osteoarthritis.
 Mental Health Issues: Feelings of low self-esteem, depression, or anxiety often accompany obesity.
Mental Health Issues: Feelings of low self-esteem, depression, or anxiety often accompany obesity.

















.jpg)
.jpg)